Is Surf Fishing Better at High or Low Tide?
Experienced anglers stress the pivotal role of tides in optimizing surf fishing experiences. The prime time for surf fishing typically aligns with the two-hour window preceding high tide, offering optimal conditions and yielding superior results. Additionally, exploring surf fishing during periods around 2 to 3 hours before and after low tide can prove fruitful, particularly in specific locations and for specific fish species. Notably, slack tide, occurring during the tide transition, tends to witness a decrease in fish activity, leading to fewer bites.
Embarking on my journey into the realm of surf fishing, I immersed myself in thorough research on tidal patterns. Despite my profound love for the ocean, I discovered nuanced details about tides that had eluded me initially. My findings comprise intriguing information poised to enhance your surf fishing escapades. Without further delay, let’s delve into the insights I’ve uncovered, potentially elevating your next surf fishing adventure.
Also Read: Cast 200 Yards Surf Fishing
What Are High and Low Tides?
The ocean experiences periodic fluctuations in water levels, alternating between high tide and low tide. The question arises: what precisely causes these variations, and is there a discernible pattern? Let’s delve into the reasons behind the phenomenon and explore whether there is a systematic pattern governing these changes.
What Causes High and Low Tide?
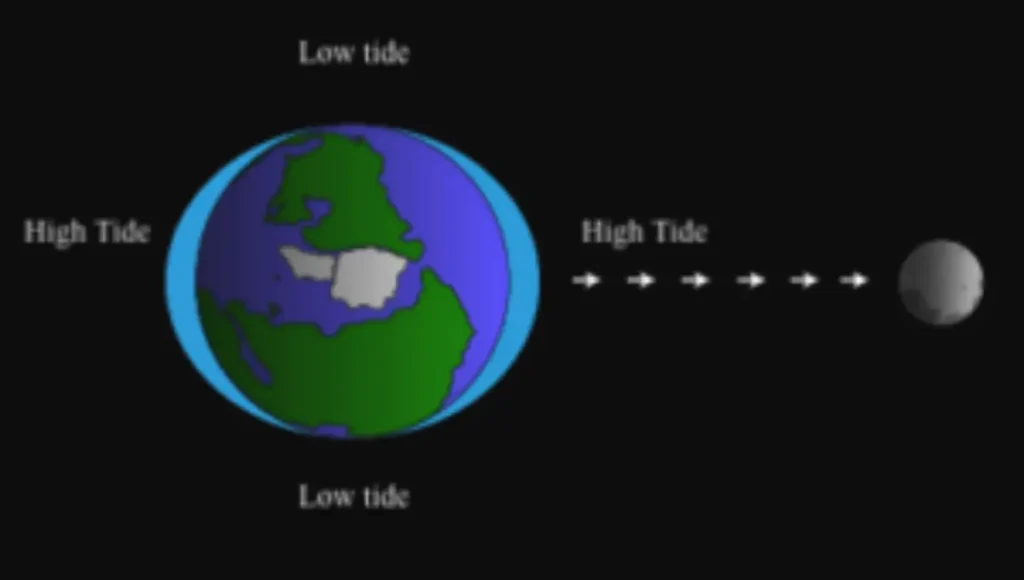
The moon’s gravitational force is responsible for generating tides on Earth. Despite its smaller size compared to Earth, the moon’s gravity has a significant impact, particularly on bodies of water. Oceans, seas, lakes, and other water masses closest to the moon experience a bulging effect.
Interestingly, even bodies of water farthest from the moon also bulge, resulting in a second high tide on the opposite side of the Earth. Consequently, areas not experiencing high tides are in a state of low tides. This implies that there are consistently two high tides and two low tides occurring simultaneously on Earth. Typically, each day, every region on Earth undergoes both high and low tide phases.
Other Things That Can Cause High or Low Tide
In addition to the daily cycle of two high and two low tides, approximately every two weeks, there are distinctive tidal patterns known as spring and neap tides.
The sun plays a crucial role in these occurrences. More extreme spring tides happen during the new moon and full moon phases when the Earth, moon, and sun align.
Furthermore, the influence of external factors such as strong winds, storms, hurricanes, and variations in atmospheric pressure can also have a minor impact on tide levels, albeit to a much lesser extent.
What Is the Best Tide for Surf Fishing?

Fish tend to be more active during specific tide levels, and there are instances where you might struggle to catch any at all. Many experienced anglers meticulously plan their surf fishing trips based on tidal conditions.
However, it’s crucial to note that there isn’t a universally ideal tide for surf fishing. The effectiveness of tides depends on various factors, including individual circumstances, locations, weather conditions, and seasons. Fish do not respond uniformly to tides, and both low and high tides can be favorable or unfavorable at different times.
Seasonal variations also play a role in the feeding behavior of fish. What works during spring or winter may not yield the same results in the summer. The key is adapting to the specific conditions.
While tides may offer advantages or disadvantages, the primary focus should be on locating the fish. Understanding and reading the beach, and identifying sandbars, cuts, and troughs are crucial aspects. Consider the tide as just one element in the broader equation of successful fishing.
Surf Fishing Strategies for Low Tide and High Tide
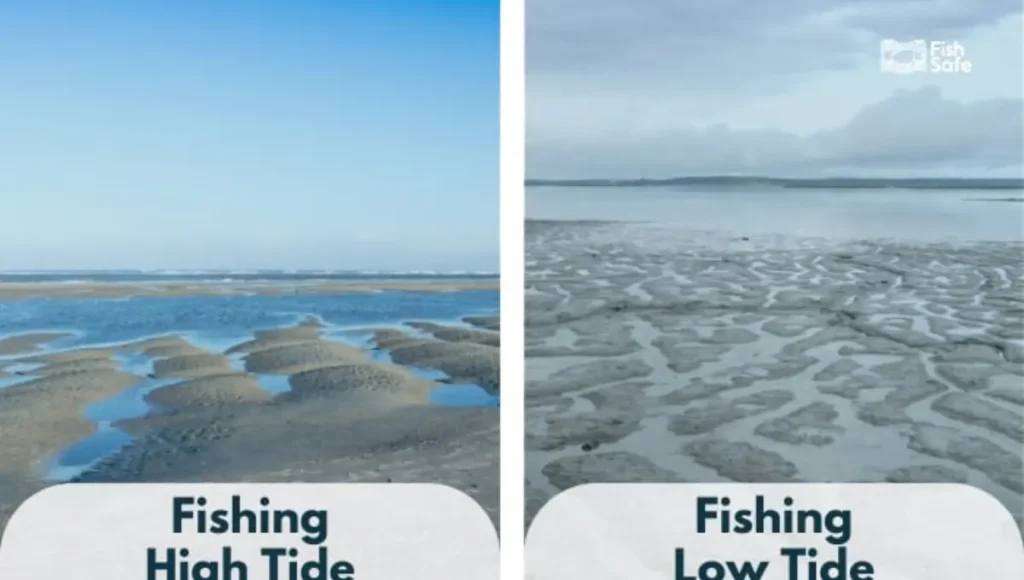

Exploring low tide areas is fascinating as it unveils potential fishing spots once the tide rises. A general guideline is to fish one to two hours before or after low tide.
During low tide, focusing on pockets and channels where predatory fish can target their baitfish proves beneficial. Similarly, for surf fishing, the recommended timeframe is one to two hours before or after high tide.
However, exceptions abound, as high tide can be a peak fishing period when fish are actively feeding. Yet, it’s important to note that high tide might disperse fish, potentially making high tide surf fishing less productive.
Spring tides, characterized by significant water movement, can pose challenges in areas with abundant structure, weeds, and other obstacles. Navigating such conditions may require additional skill and effort while fishing.
Incoming vs. Outgoing Tides
The prevailing belief is that the impending high tide offers the prime window for surf fishing. The presence of moving water generally enhances the chances of getting more bites. Specifically, incoming or outgoing tides are considered optimal for surf fishing, while slack tides are typically regarded as less favorable.
As mentioned earlier, many anglers steer clear of fishing during the peak points of the tide – either the highest or the lowest. The tidal ranges can exhibit considerable variation depending on the surf fishing location. Excessively high water currents can pose challenges, making surf fishing quite difficult under such conditions.
How Tides Affect Fish
Aligning your fishing with the tides, while not obligatory, holds significant importance, especially in surf fishing.
The behavior of the majority of fish revolves around three key factors: feeding, comfort, and spawning. Among these, the tide notably influences one of the most crucial aspects of fish behavior – their feeding patterns.
In pursuit of predatory fish, it’s observed that they are often caught during high tide, actively seeking to feed on baitfish, particularly in areas with pockets. Predatory fish are known for their constant movement, adapting their location as the tide changes.
During low tide, their focus shifts to areas where baitfish concentration is highest. These are the spots where baitfish traverse as they return with the receding low tide.
Is the Tide Important for Surf Fishing?

Overemphasizing the tide alone is a common mistake, as surf fishing entails considering multiple variables beyond the rising tide. The complexity goes beyond solely monitoring tide conditions.
For an accurate prediction of your surf fishing experience, it’s essential to factor in various elements such as
While tides undeniably influence fish behavior, their impact varies across different areas and specific tides. However, one of the critical aspects of surf fishing is the direction and strength of the current. The current’s characteristics play a pivotal role, in determining whether keeping bait in the optimal fishing zones will be easier or more challenging.
How Do the Tides Ranges Vary?
Understanding tides, though crucial, can be challenging due to significant variations in what constitutes high and low tides, particularly in different regions.
The disparity in tidal patterns is evident across various coasts. This discrepancy is quantified as the tidal range, representing the difference between low and high tide. Here are approximate mean tidal ranges for different areas:
Alaska, with its unique geography, exhibits fascinating tidal ranges:
How to Check the Level of the Tide and Other Variables
In today’s era of advanced technology, much of the guesswork in fishing can be eliminated with the use of online platforms.
A highly recommended tool is Tides4fishing.com, an excellent online platform providing predictions for nearly every factor influencing fishing productivity.
It’s essential to note that these are averages and predictions, subject to variations due to weather changes, which can significantly impact fishing success.
For those seeking a simpler approach focused solely on tide timings, the free smartphone app “Tides Near Me” is an excellent solution for real-time tide monitoring. Additionally, obtaining a tidal chart from a local tackle shop is another reliable option.
Having effective means to predict tides can be the key difference between a successful fishing trip and heading home empty-handed.
The Tidal Current
The primary consideration when evaluating tidal conditions is the current.
On the tidal chart, the numbers indicate the expected water level changes, with a steeper angle or larger number signifying faster movement and, consequently, a stronger current. Anglers, particularly those engaged in deep fishing, may prefer to avoid areas with fast waters.
A useful method to estimate current strength is to examine the difference between low tide and high tide. Typically, there’s approximately a six-hour span between these points, although this duration can vary.
For instance, if the low tide is 1 foot and the subsequent high tide is 5 feet, there will be a substantial increase from one to five feet over six hours, resulting in a robust current and significant water movement.
Contrastingly, if the low tide is 2.5 feet and the impending high tide is expected to be 3.2 feet, the water will only rise by 0.7 feet in the next six hours. This scenario indicates a much calmer water state with minimal current.
The Tidal Coefficient
Another valuable tool for assessing tidal conditions is the tidal coefficient. This factor is instrumental in predicting the strength of the current and indicates the expected high or low tide levels.
The tidal coefficient typically ranges from 20 to 120. A higher number signifies a greater difference between low and high tide, indicating more substantial water movement and increased current strength.
Is it worth fishing at low tide?

Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
While both high and low tides offer advantages for surf fishing, most anglers agree that low tide generally provides better conditions. During low tide, more of the seafloor is exposed, allowing fish to feed closer to shore where they are more accessible to surf casters. Baits and lures have less water to travel through reaching the feeding fish.
Anglers also face less battling of waves and currents at low tide. However, high tide can concentrate baitfish and gamefish in narrow channels between the shore and first sandbars, offering opportunities as well. The best approach may be to fish both tides, as conditions vary depending on location, weather, and other environmental factors.






